

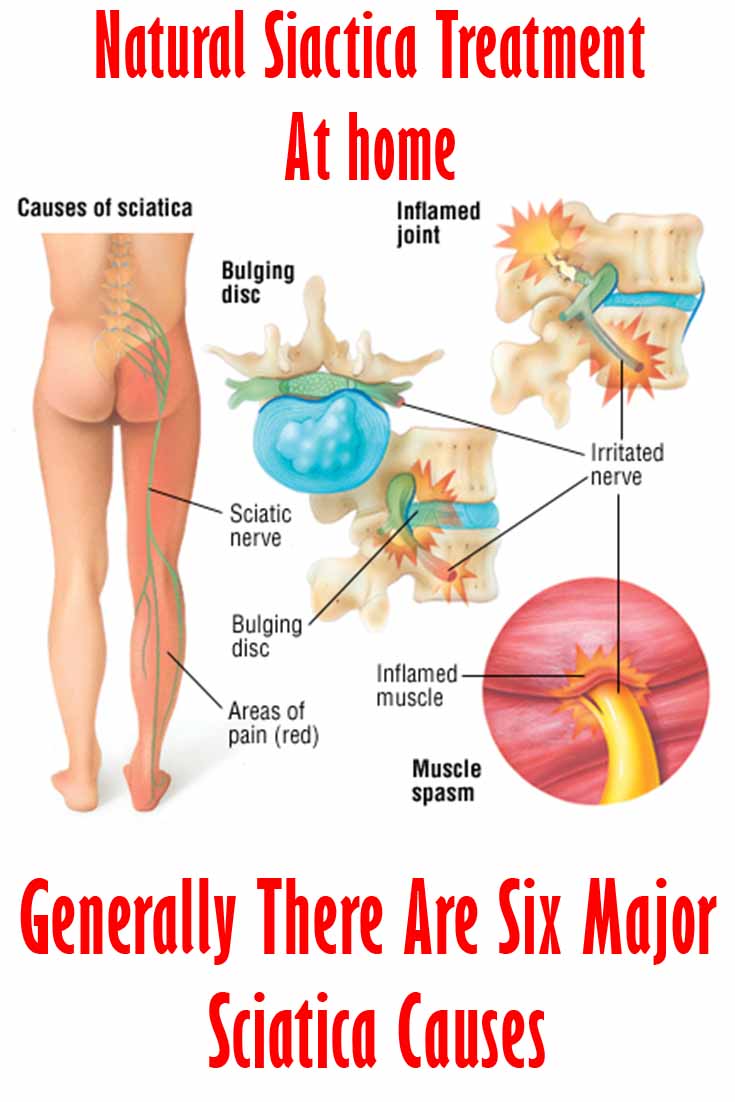
Efficacy of coblation annuloplasty in discogenic low back pain: a prospective observational study. Sometimes, degenerated discs may cause nerve tissues to grow into the disc, penetrating the outer and inner layers of the disc, causing sciatica pain.ĥ He L, Hu X, Tang Y, Li X, Zheng S, Ni J. Epidemiology, pathophysiology and symptomatic treatment of sciatica: A review. Hyaluronic acid fragments enhance the inflammatory and catabolic response in human intervertebral disc cells through modulation of toll-like receptor 2 signalling pathways. , 3 Quero L, Klawitter M, Schmaus A, et al. Mechanisms of low back pain: a guide for diagnosis and therapy. These chemical irritants are thought to include substances like hyaluronic acid and/or fibronectin (protein) fragments that leak out of degenerated or herniated discs.Ģ Allegri M, Montella S, Salici F, et al. Research indicates that chemical irritants may cause inflammation and/or irritation of the sciatic nerve. Rarely, tumors, cysts, infection, or abscesses in the lower spine or pelvic region may compress the sciatic nerve Instability of a vertebral segment that occurs if one vertebra slips over the one below it (spondylolisthesis), vertebral defects ( spondylolysis), or complete dislocation of one or more vertebrae may directly compress the nerve root(s) of the sciatic nerve. Other degenerative changes in the spine, such as thickening of facet joint capsules and/or ligaments, may also directly compress the sciatic nerve. Stenosis, or narrowing of the intervertebral opening through which the sciatic nerve roots travel, may compress or irritate the sciatic nerve. A disc in the lower back may bulge or herniate, causing irritation, and/or compression of a sciatic nerve root. Several common factors may affect the sciatic nerve: Mechanical compressionĭirect physical forces may be applied to the nerve due to the following common conditions:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
